Patents - EUON
Energy
Overview
This section looks at the patenting activity in the field of nanotechnology and energy between 2017-2020. Granted patents and patent applications focused on energy and nanotechnology were extracted from the general collection of nanotechnology patents in 2017-2020 developed by the study team for the database. The patents were collected from Espacenet database maintained by the European Patent Office.
The dataset of patents on energy and nanotechnology was developed by extracting the granted patents and patent applications that contained the CPC classes and sub-classes dedicated to energy in their bibliographic information. It should be noted that most nanotechnology patents contain multiple classes in their subject descriptions. In CPC energy is covered under Y02E class (reduction of greenhouse gas [GHG] emissions, related to energy generation, transmission or distribution).
| Table AIV-2: Energy in the Cooperative Patent Classification (CPC)1 | |
|---|---|
| Class | Title |
| Y02E 10/00 | Energy generation through renewable energy sources |
| Y02E 60/10 | Energy storage using batteries |
| Y02E 60/30 | Hydrogen technology |
Patents on nanotechnology in energy
As a result of patent collection mining, 4,856 patent applications and granted patents published between 2017-2020 were identified. The number of patents and patent applications containing energy classifications slightly varied each year. In general, the data shows a very similar level of interest to this topic over the period under analysis.
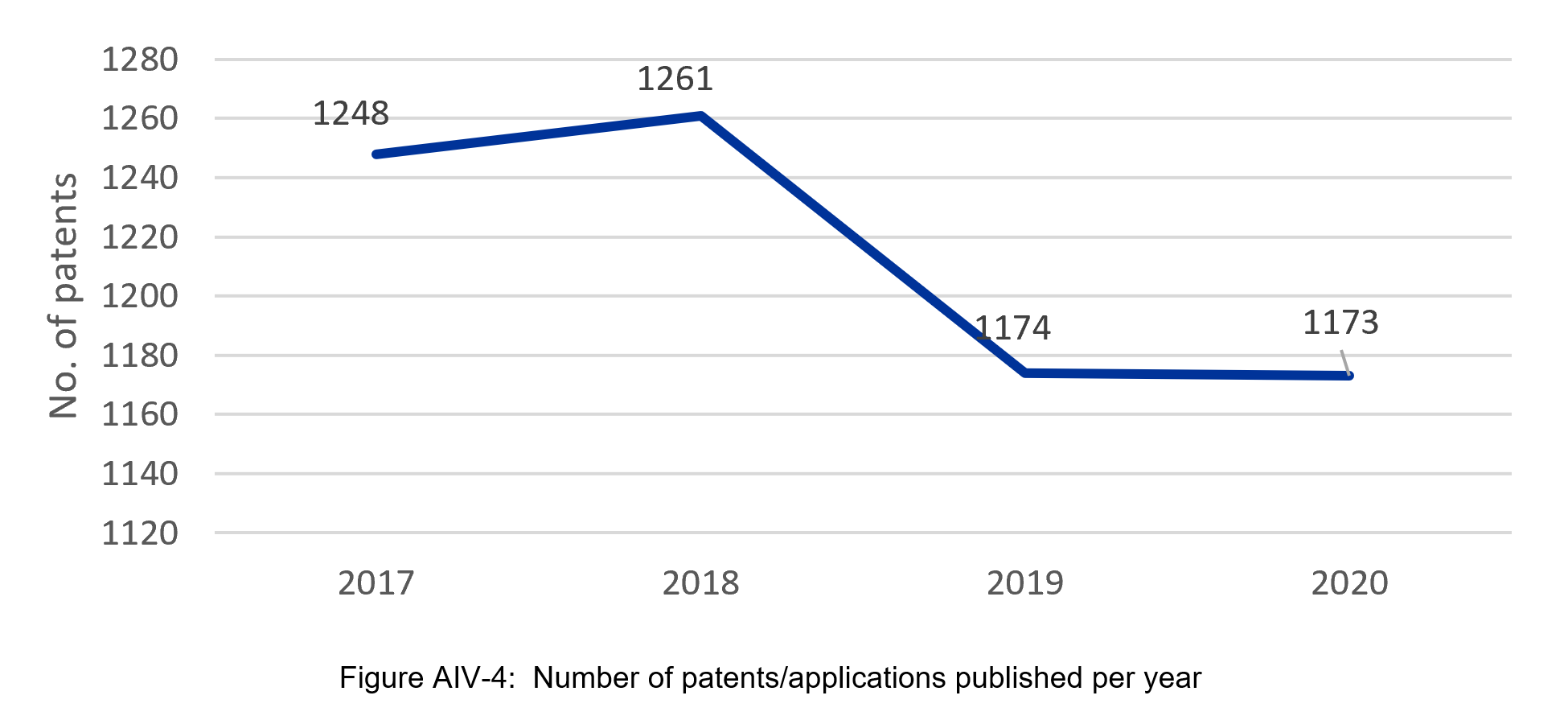
Most patents (4,524, 93%) were published in the national patent offices, while the rest were in the World Intellectual Property Organisation (WIPO, 277, 6%) and the European Patent Office (55, 1%).
China (4,110 applications, 85%) prevailed among the countries where most patent applications were published. Other countries, such as the USA, South Korea, Japan, and Russian Federation, were in top five by the number of published applications, but significantly lagged behind China.
| Table AIV-3: Top-five countries by files patents/applications in agriculture and nanotechnology in 2017-2020 | |
|---|---|
| Country | No. of patents/patent applications, % |
| China | 4 110, 85% |
| USA | 220, 5% |
| South Korea | 91, 2% |
| Japan | 40, 1% |
| Russian Federation | 17, 0.3% |
Patent applications and granted patents contained two of three CPC sub-classes referring to energy. The analysis did not identify any patents focused on Y02E60/30 Hydrogen technology in 2017-2020.
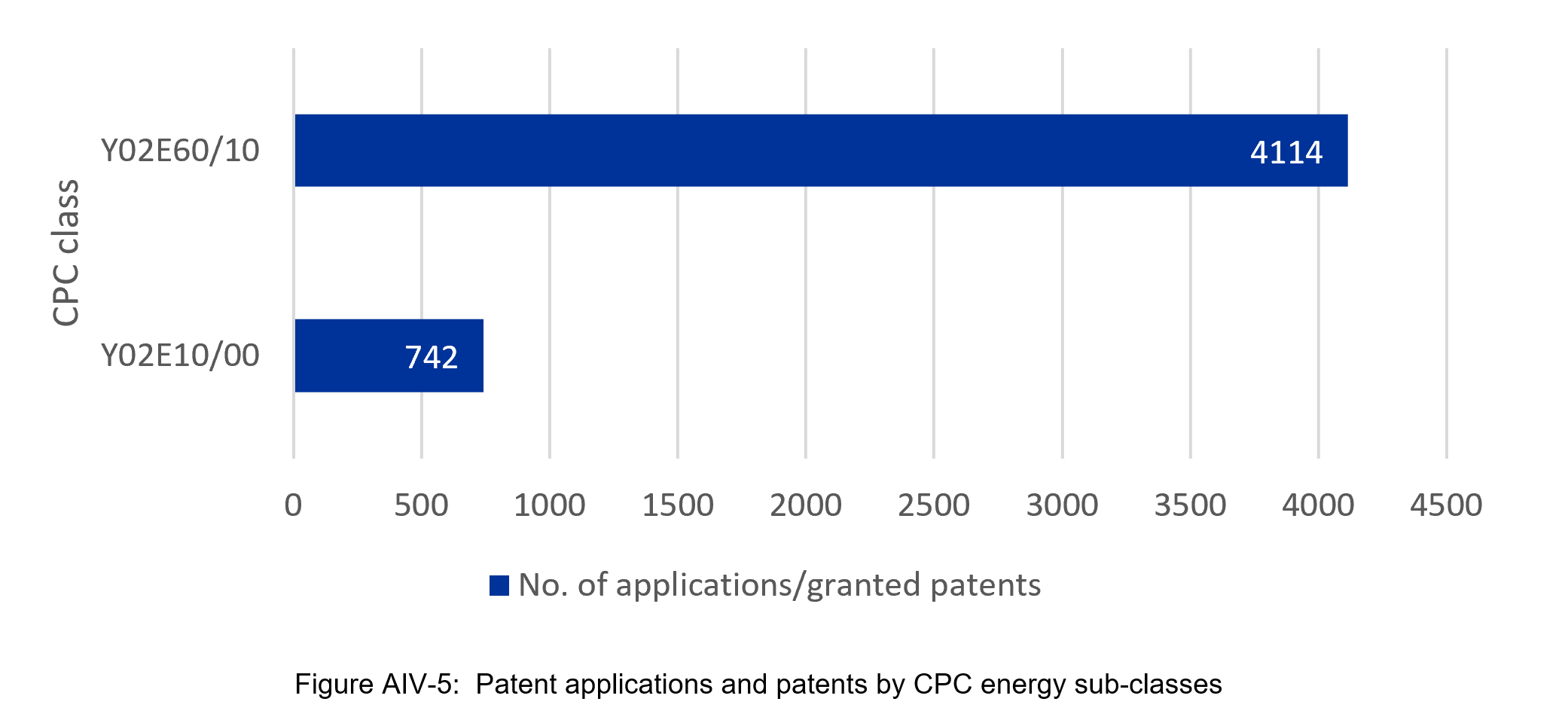
The overwhelming majority of patents and patent applications focused on Y02E60/10 (Energy storage using batteries) – 4,114 (85%), while only 742 – on Y02E60/10 (Energy generation through renewable energy sources).
| Table AIV-4: Examples of patents focused on Y02E60/10 sub-class | |
|---|---|
| Bibliographic information | Abstract |
| Chu, H. et al. (2020). Negative active material and negative electrode and lithium battery including the material. Patent no. US10553865B2. Available here. (Granted patent) | A negative active material includes a silicon-based alloy, and the silicon-based alloy includes a Si single phase, a FeSi2 alpha phase, and a FeSi2 beta phase, wherein an intensity ratio of a second diffraction peak of the FeSi2 beta phase to a first diffraction peak of the FeSi2 alpha phase may be 0.1 or higher. A negative electrode includes the negative active material and a lithium battery includes the negative electrode. Lifespan characteristics of the lithium battery including the negative active material may improve. |
| Kovalenko, M. et al. (2017). Method for the Production of Msnx Nanoparticles as Anode Materials for a Rechargeable Battery. Patent no. EP3124137A1. Available here. (Granted patent) | The invention relates to a method for the production of MSnxnanoparticles, wherein M is an element selected from the group consisting of Co, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu, In, Al, Ge, Pb, Bi, Ga, and 0 < x ≤ 10 said method comprising the steps of:- synthesizing Sn nanoparticles by reducing a tin salt with a solution of a hydride in an anhydrous polar solvent, separating the solid Sn nanoparticles formed from the solution, and washing the Sn nanoparticles,- synthesizing M nanoparticles by reducing a metal salt with a solution of a hydride in an anhydrous polar solvent, separating the solid M nanoparticles formed from the solution, and washing the M nanoparticles,- mechanical mixing said Sn nanoparticles and said M nanoparticles to convert them into MSnxnanoparticles. |
Energy innovation breakthroughs in patents
Innovation breakthrough is a particular type of innovation that has a profound effect on subsequent inventions, products and services. Three indicators of patents were studied to identify innovation breakthroughs – number of forward citations, number of citing organisations and number of citing countries.
Two patent applications met the criteria of innovation breakthrough. The application by Huang et al. (2018) was prepared by Shaanxi University of Science and Technology (China) and received 12 citations from 7 organisations operating in 2 countries. However, according to the newest EPO data (as of 8 April 2022) the invention patent was rejected.2
| Table AIV-5: Breakthrough patent application in energy | |
|---|---|
| Bibliographic information | Abstract |
| Huang J. et al. (2018). Preparation method of nitrogen-sulfur co-doped three-dimensional graphene, prepared product and product application thereof. No. CN108470890A. Available here. (Patent grant rejected) | The invention provides a preparation method of nitrogen-sulfur co-doped three-dimensional graphene. Graphene oxide is dispersed in deionized water to obtain graphene oxide dispersion liquid, and melamine powder and an ethanol solution of trithiocyanuric acid are added, uniformly dispersed and then placed into a hydrothermal reactor for hydrothermal reaction; hydrothermal products are dried, and finally heat treatment is conducted. The invention further provides the nitrogen-sulfur co-doped three-dimensional graphene and application of the graphene as an electrode material. The prepared producthas nitrogen element content of 3-10% and sulfur element content of 0.5-3%. The preparation method has the advantages that an experimental method is safe, non-toxic, low in cost and simple to operate. A hydrothermal method is adopted to achieve doping, three-dimensional construction and graphene oxide reduction. The prepared three-dimensional graphene has a large specific surface area and can be applied in the fields of lithium-ion batteries, supercapacitors, electrocatalysis and the like. |
| Moon, J. et al. (2019). Silicon-containing structure, method of preparing the same, carbon composite using the same, and electrode, lithium battery, and device each including the same. No. EP3518328A1. Available here. (Granted patent) | A silicon-containing structure including: a silicon composite including a porous silicon secondary particle and a first carbon flake on a surface of the porous silicon secondary particle; a carbonaceous coating layer on the porous silicon composite, the carbonaceous coating layer comprising a first amorphous carbon; and the silicon composite comprises a second amorphous carbon and has a density that is equal to or less than a density of the carbonaceous coating layer, wherein the porous silicon secondary particle includes an aggregate of silicon composite primary particles, each including silicon, a silicon suboxide on a surface of the silicon, and a second carbon flake on a surface of the silicon suboxide. |
The patent by Moon et al.3 was prepared by Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. (South Korea) and received 4 citations from 3 organisations operating in 3 countries.
1 European Patent Office. (2022). Cooperative Patent Classification, Y: Reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, related to energy generation, transmission or distribution. Available at: https://www.cooperativepatentclassification.org/sites/default/files/cpc/scheme/Y/scheme-Y02E.pdf
2 For details see legal events in the application data: Jianfeng, H., Qiao, X., Jiayin, L., Liyun, C., Yayi, C., Hui, Q., Ling, G., & Huan, D. (2018). Preparation method of nitrogen-sulfur co-doped three-dimensional graphene, prepared product and product application thereof (CN108470890A). European Patent Office. Available at: https://worldwide.espacenet.com/patent/search/family/063265366/publication/CN108470890A?q=pn%3DCN108470890A
3 Moon, J. et al. (2019). Silicon-containing structure, method of preparing the same, carbon composite using the same, and electrode, lithium battery, and device each including the same. No. EP3518328A1. Available at: https://worldwide.espacenet.com/patent/search/family/065228387/publication/EP3518328A1?q=pn%3DEP3518328A1


